CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps
The Most Detailed Description of Subnets
I believe many beginners may be stuck by subnet division when they first contact with network engines, even some working for a long time also can only rely on a variety of IP address calculators. The computer is not as convenient as us to plan. rest assured, and we can only understand the subnet division to deeply understand the related knowledge of routing. Let`s study it together.
Step 1: Knowing the IP address and subnet mask
First of all, we come to see the most common IP address 192.168.1.1, whose representation is in decimal notation, and separated by a “dot”, called dotted decimal notation.The reason is to make it easier for people to read, since humans are more familiar with the decimal system. In computers and network devices, IP addresses are represented in binary form. For example, if we convert 192.168.1.1 above to binary, we will get something like this:

We can see that the full length of an IP address is 32 bits, and each point is divided into 8 bits, which is called an octet. However, this is not the whole picture of an IP address, because subnet masks often appear together with IP addresses。

If the IP address is configured on a computer, the subnet mask is automatically generated as 255.255.255.0. The subnet mask identifies the network bit and host bit of an IP address. The 1 in the subnet mask corresponds to the network bit, and the 0 in the subnet mask corresponds to the host bit. The 1 and 0 in a subnet mask must be consecutive, so there is another way to represent a subnet mask, depending on how many consecutive 1 are in the subnet mask. For example, the subnet mask above can also be represented as /24. This notation is called prefix notation.
If all the host bits are 0, the IP address is called the network number and used to identify the network segment. When all the host bits are 1, the IP address is called a broadcast address and is used for broadcasting within this network segment. For example, according to this rule, 192.168.1.1/24 belongs to network segment 192.168.1.0. The broadcast address of this network segment is 192.168.1.255. Note: Neither the network number nor the broadcast address can be configured on the host.
CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps
Step 2: Understanding the main class network
Why is the default length of the subnet mask for the above IP address 24? The reason is that it is a class C IP address. But how to distinguish which types such as ABCDE class does the IP address belong to?

We only need to convert the IP address to base 2 for observation. If the IP address starts with 0, it is A-class address and the subnet mask length is /8; if the IP address starts with 10, it is B-class address and the length of the subnet mask is /16; if the IP address starts with 110, it is C-class address and the subnet mask length is /24; if the address starts with 1110, it is a D-class address, which is used for multicast. E-class addresses are reserved for experiments. In addition, network segment 127.0.0.0 is a loopback test address, so it cannot be assigned to hosts.
Different primary networks have different default subnet mask lengths and are used to different host bits. The total length of the Ip address is 32 bits, so under a class C /24 subnet mask, there are only 8 host bits available, which is 2 ^ 8, or 256 hosts. However, when calculating the number of available hosts, remember to subtract the network number and broadcast address. That is to say, the number of available hosts in a network segment of class C address is 256 deducts 2, 254.
Step 3: Dividing IP addresses
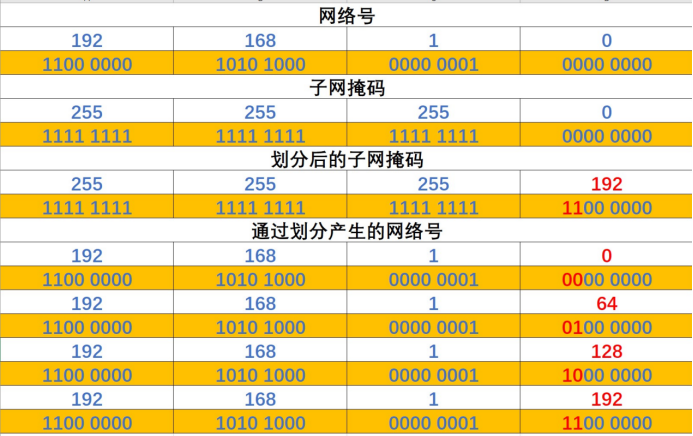
Suppose we need four network segments, but only one network segment, 192.168.1.0, is used to allocate. In this case, we can modify the subnet mask to borrow from the host bit, so that part of the host bit becomes the network bit. Here we borrow two, there are 00, 01, 10, 11 four changes, namely divided into four network segments, and each network segment can accommodate the same number of hosts, which is 2 to the sixth minus 2 hosts, that is 62. This idea of averaging is called fixed-length subnet mask partitioning (FLSM). If you feel that the IP address is not fully used, you can further divide the subnet in the same way. For example, 192.168.1.128/26 can be further divided into 192.168.1.128/27 and 192.168.1.160/27. This method, called variable length Subnet Mask partitioning (VLSM), can improve the utilization of IP addresses well.
The Most Detailed Description of Subnets
CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps CCIE Dumps

